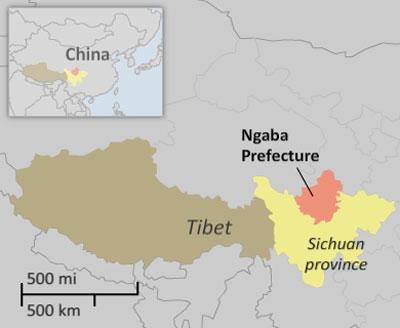
Genocide Declared, Now What?

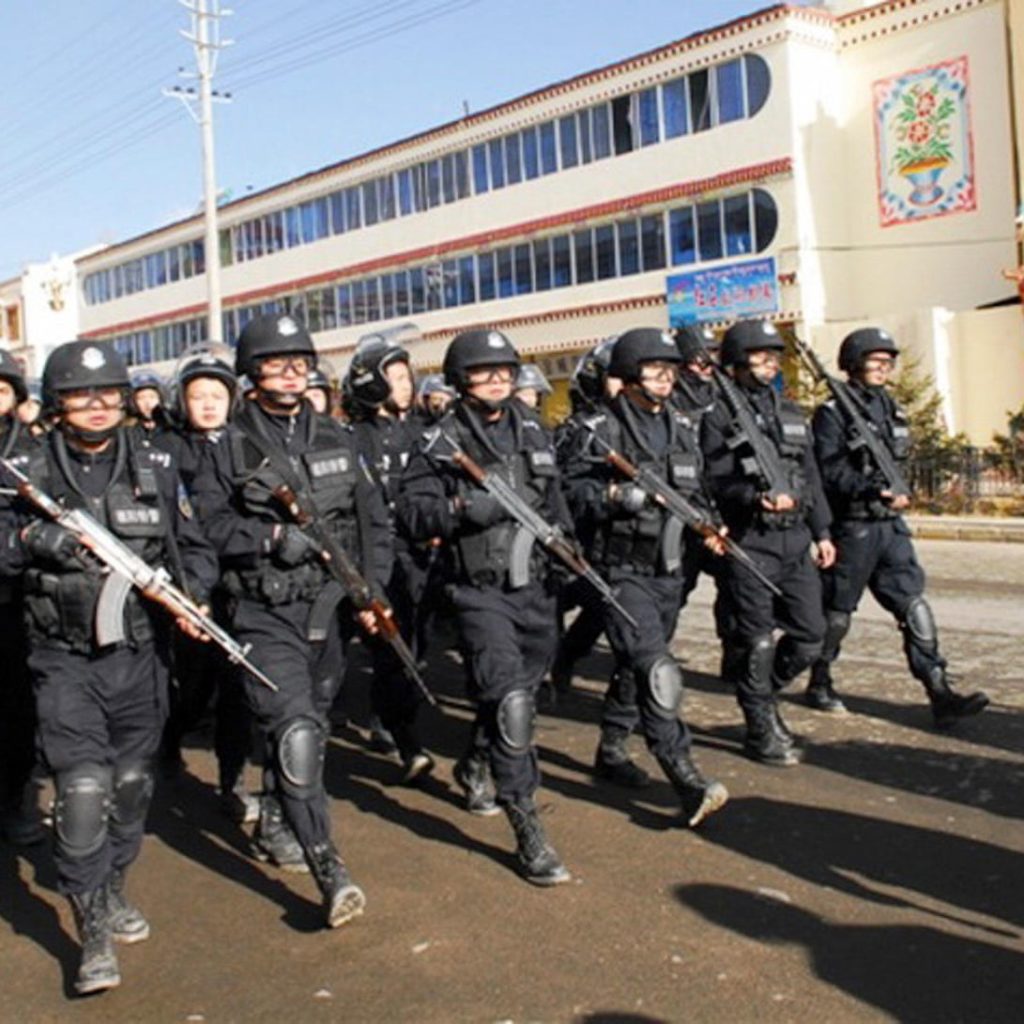
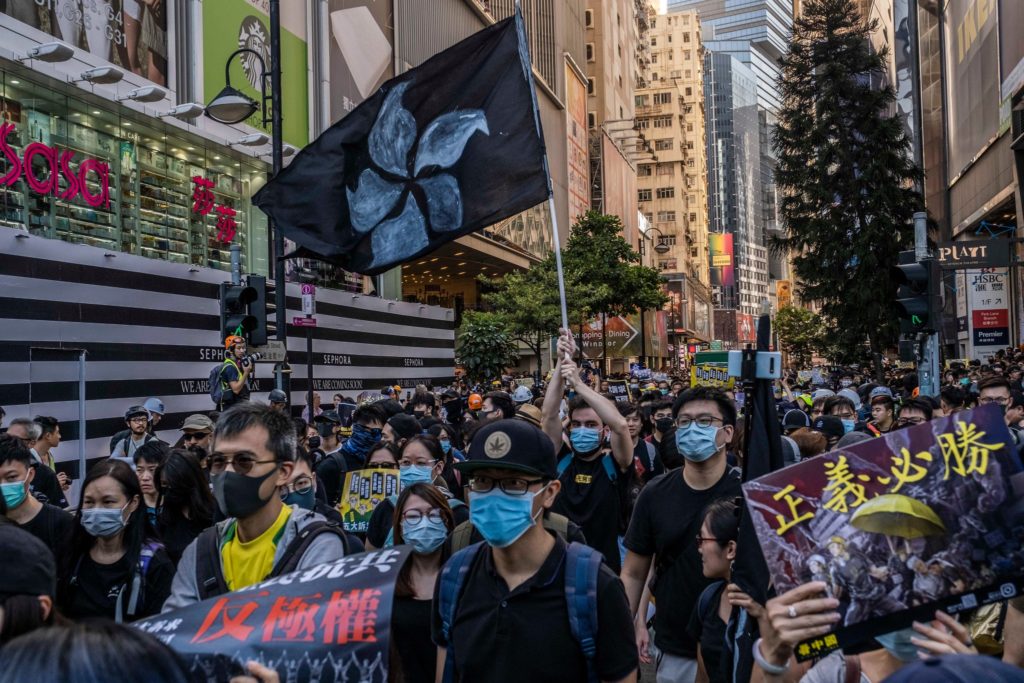
In one of his last acts as Secretary of State, Mike Pompeo stated that the Chinese government’s extrajudicial internment of 1.8 million Uyghurs, the torture and forced labor of Uyghur detainees, and the forced sterilizations and abortions of Uyghur women, amounts to crimes against humanity and genocide. Hours later, in his confirmation hearings, President-elect Biden’s secretary of state nominee Antony Blinken agreed with Pompeo’s designation of genocide. Immediately, the U.S. press heralded the bi-partisan nature of this genocide declaration.
But genocide is not just about the acts committed; it also requires government intent to physically or biologically destroy the group. See Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (“In the present Convention, genocide means any of the following acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group”) (emphasis added). By declaring genocide, the U.S. government could easily get bogged down in this required element, an element that even Pompeo left out of his declaration. Nowhere in his statement does Pompeo assert that the Chinese government had an intent to physically destroy the Uyghur people.

That is why Pompeo’s declaration that the Chinese government’s actions in Xinjiang province amounts to crimes against humanity is more actionable, and has been for the past couple of years. Like genocide, crimes against humanity include acts that attack the very soul of a people and its culture: murder, extermination, torture, arbitrary detention, forcible transfer of a population, rape, sexual violence, forced sterilizations, apartheid. But unlike genocide, these crimes do not require an intent to biologically destroy. Instead, acts that constitute crimes against humanity merely need to be part of a widespread or systemic attack directed at a group, with the perpetrator’s knowledge that his or her acts are part of this larger attack. In looking at Pompeo’s declaration of genocide he states that “we are witnessing the systematic attempt to destroy Uyghurs.” In those words, he seems to mistake the element of crimes against humanity for genocide.
This isn’t to say that the crime of genocide is not occurring in Xinjiang nor that such a declaration is inconsequential. It certainly carries meaning and should. But the U.S. must ensures that it acts on these declarations and not just get caught up in a war of words with China and its allies, something that could more easily happen by solely focusing on genocide. In fact, the United Nations, through a 2005 Resolution signed by all 193 member states, requires countries to respond similarly to both genocide and crimes against humanity. For both, states have a duty to “protect populations from genocide, war crimes, ethnic cleansing and crimes against humanity” and must “use appropriate diplomatic, humanitarian and other peaceful means.” See ¶¶ 138-39.

To fulfill this obligation to protect, the U.S. must step up its efforts. Pompeo’s statement, while full of important policy pronouncements, provided no new courses of action. Similarly, Blinken’s suggestions on how to respond – ensure that we don’t import cotton picked by forced labor and guarantee that we don’t sell surveillance technologies to China – didn’t break new ground. Instead, the U.S. should be advocating a liberal asylum/refugee policy for Uyghurs.
More obvious, the U.S. government needs to start discussing boycotting the 2022 Winter Olympics in Beijing and encourage allies to do the same. How can the U.S. send its athletes to compete in games hosted by a country engaging in crimes against humanity and genocide? To do so would render Pompeo and Blinken’s statements today hollow words and would embolden the Chinese government – and all governments – to continue genocidal policies. The last time we ignored the genocidal intent of a host country – Berlin, 1936 – six million Jews were murdered by the governing party. The 2022 Winter Olympics are a little more than a year away. In fairness to our athletes, these discussions must begin now. Also, making these discussions public now, might save some lives in Xinjiang.

But the U.S. cannot go this alone, either boycotting the 2022 Olympic boycott or fulfilling its responsibility to protect. Only a multilateral response can defeat crimes against humanity; no individual country has ever been able to end a genocide. The U.S. must re-engage international institutions including re-joining the U.N. Human Rights Council, a body where has been dominated by China since the U.S.’ 2018 withdrawal from the Council.
Genocide is a bold word. Those words need to be followed up with bold action. Failure to do so only weakens those post-World War II international institutions and treaties the Biden Administration has promised to uphold. It also means that Uyghurs will continue to suffer while all we did was play word games.
 On Facebook
On Facebook By Email
By Email